07 Nov, 2025
Feel free to reach out to us.

07 Nov, 2025

This article is medically reviewed by Dr. V. S. N. Rao, Senior Consultant - Radiation Oncology, HCG Cancer Centre, Vijayawada.
Radiology, radiotherapy, and radiodiagnosis can be confusing for many, as they seem related. While this is somewhat true, there are quite a few differences between these disciplines.
The internet is flooded with queries like the difference between radiology and radiotherapy, radiology vs. radiotherapy, or whether radiology and radiotherapy are the same.
In this blog article, let us try to understand how one discipline is different from the other and how each has an important role in managing various diseases, including cancer.
Radiology is a medical field that uses imaging to diagnose and treat illnesses. Radiology procedures use small amounts of radiation to safely produce pictures of the internal structures in the body.
Radiologists have expertise in analyzing detailed images of the body’s internal structures produced by different scanning methods to identify diseases at their early stages for appropriate disease management.
Radiology is further categorized into two broad disciplines based on their applications: diagnostic radiology and interventional radiology.
Diagnostic radiology is a radiology discipline that focuses on diagnosing various types of diseases, using procedures like X-rays, ultrasound scans, MRI scans, and CT scans.
The scans involve minimal to negligible radiation exposure, and they are non-invasive.
Interventional radiology is a discipline of radiology that focuses on performing minimally invasive, image-guided interventions to collect tissue samples from various parts of the body and to perform minor procedures as part of disease management.
Examples of interventional radiology procedures include stent placement, embolization, drainage procedures, ablation procedures, and more.
Additional Reading: What are Interventional Radiology Procedures and Treatments
Radiology is essential for diagnosing diseases, monitoring conditions, and guiding medical procedures. Without this discipline, modern healthcare would lack the ability to detect conditions early and provide timely treatment.
The ability to see inside the human body without surgery has transformed medicine, reducing risks and improving outcomes for patients.
Interventional procedures like angioplasty and stent placement, which are guided by imaging during minimally invasive surgeries, positively impact the health outcomes and the quality of life for patients.
Radiodiagnosis is the field of medical science that focuses on detecting and diagnosing a wide range of health conditions with the help of different imaging techniques.
The terms radiology and radiodiagnosis are often used interchangeably. However, it is important to note that radiology is a broader discipline that focuses on diagnosis and interventions, whereas radiodiagnosis is a narrower discipline that focuses on detection and diagnosis only.
X-ray imaging is the most common radiodiagnosis or imaging procedure. X-rays are a form of electromagnetic radiation that carries high energy. This imaging technique creates pictures mainly of bones and some other tissues.
Fractures, tumors, and infections like pneumonia can be diagnosed through an X-ray scan. In the emergency department, X-rays are extensively employed for the quick identification of trauma and intra-abdominal injuries.
MRI uses powerful magnetic fields and radio waves to create clear pictures of internal body parts. It is better for repeated scans as it does not involve ionizing radiation, like X-rays.
It is particularly effective in examining the brain, spinal cord, and muscles, providing high-resolution images that reveal complex conditions like multiple sclerosis and brain tumors.
CT scans are a combination of X-rays and computers that produce pictures of the inside of the body. It is a sensitive method that is applied in identifying tumors and internal bleeding, as well as bone fractures.
CT scans are important in the determination of diseases such as strokes, infections, and cancer.
Radiodiagnosis is essential for the accurate diagnosis of a wide range of health conditions, including cardiovascular diseases, neurological disorders, infections, fractures, trauma, and cancer.
These procedures are non-invasive and safe for patients, as they only use small amounts of radiation to produce images. These imaging techniques are also used for disease staging, radiotherapy treatment planning, and treatment response monitoring.
Accurate diagnosis is essential for planning appropriate interventions for each case and achieving desirable health outcomes.
Radiotherapy, also called radiation therapy, is a cancer treatment that uses high-energy radiation to destroy cancer cells. It is also referred to as therapeutic radiology.
The purpose of radiotherapy is to eliminate cancer, shrink tumors before surgery, destroy residual cancer cells to reduce recurrence risk, and alleviate symptoms caused by advanced-stage cancers to improve the quality of life.
Radiotherapy is used for different types of cancer, and different techniques of radiotherapy may be used based on individual case factors.
Additional Reading: What is Radiation Therapy - Procedure, Tests & Risks
During internal radiotherapy, or brachytherapy, a radioactive source is positioned within or close to the tumor. This technique is often used in prostate, cervical, and certain breast cancers.
The brachytherapy approach ensures that the tumor receives a large radiation dose but with little exposure to the surrounding healthy tissues.
EBRT uses high-energy beams directed at tumors from outside the body. It is a widely used radiotherapy technique for treating lung, breast, and brain cancers.
External beam radiation therapy is used for targeted radiation delivery, reducing side effects, and improving treatment outcomes. Significant advancements have been made in the field of EBRT to improve the overall treatment outcomes. Different techniques used during EBRT include VMAT, IMRT, IGRT, SRS, and SBRT.
Radiotherapy is one of the crucial pillars of cancer management. It can be applied before or after surgery, in combination with chemotherapy, or as a standalone therapy. It helps control the spread of cancer, relieves symptoms in advanced stages, and can even cure certain types of tumors.
Radiation therapy is getting better as technology advances. For instance, we have the CyberKnife radiotherapy platform, which requires only 2-5 sessions to treat cancer, unlike other platforms that need up to 40 sessions. The image guidance feature in many radiotherapy platforms allows for more precise targeting and treatment delivery.
Technologies today allow for more precise radiotherapy treatment planning and adaptive planning, which helps reduce damage to healthy tissues in the body.
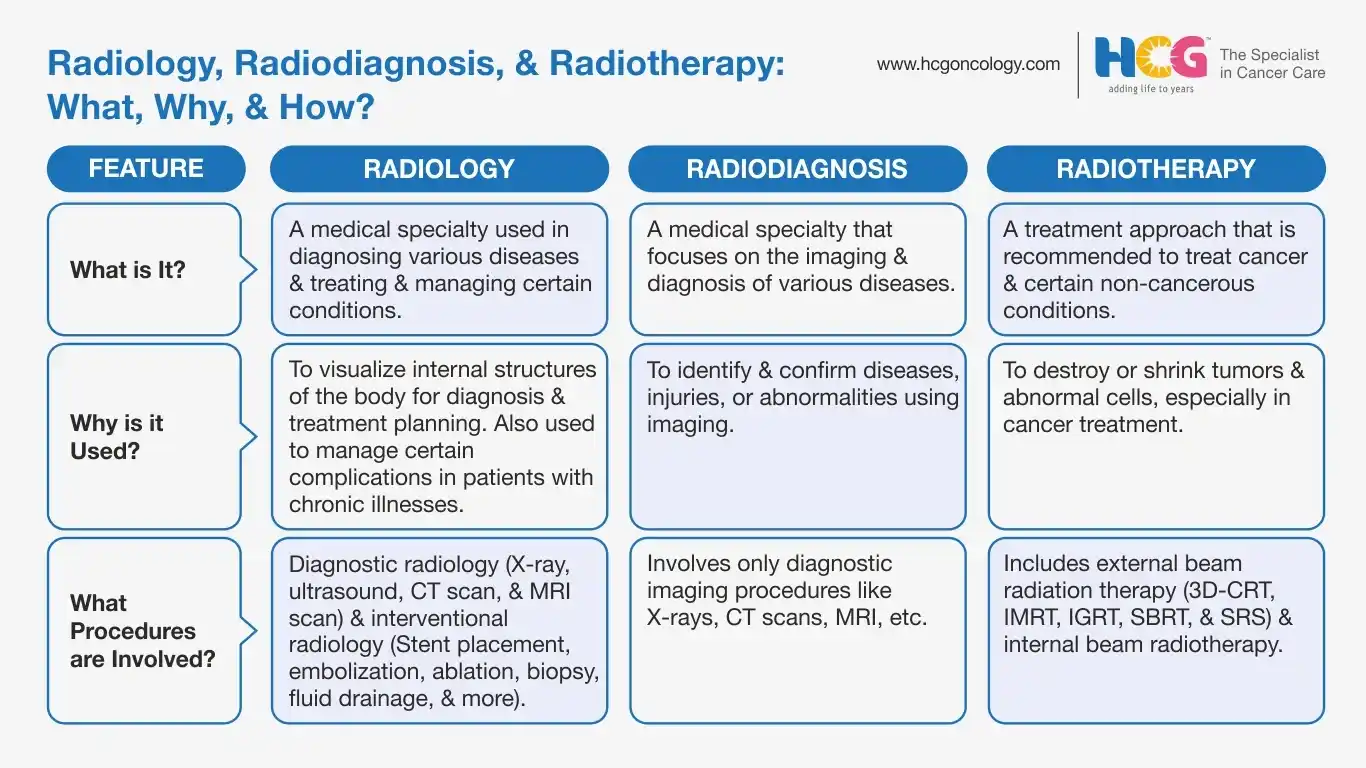
The following table clearly elucidates the differences between radiology, radiodiagnosis, and radiotherapy:
| Parameters | Radiology | Radiodiagnosis | Radiotherapy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purpose | To diagnose different types of health conditions, including cancers, and manage them through minimally invasive procedures. | To diagnose different types of health conditions using various imaging techniques. | Primarily to treat different types of cancer using high-intensity radiation beams, it is also used to treat certain benign conditions. |
| Techniques | Imaging techniques like X-rays, ultrasound, MRI scans, CT scans, and interventional radiology procedures like embolizations, ablations, drainage procedures, stent placements, and biopsies | X-rays, ultrasound, MRI scans, and CT scans are used. | External beam radiation therapy and internal beam radiation therapy (brachytherapy). |
| Specialists Involved | Radiologists and interventional radiologists | Radiologists | Radiation oncologists |
| Duration | 1-2 hours, depending on the procedure | 15–60 minutes, depending on the specific procedure | 10–45 minutes per session; number of sessions may vary. |
| Radiation Exposure | Low | Low | High |
| Outcome | Accurate diagnosis of disease, disease staging, treatment planning, and management of certain disease complications. | Accurate diagnosis of disease, disease staging, and treatment planning. | Controlling cancer growth, alleviating cancer symptoms in advanced stages, and reducing relapse risk. |
Many ask, which is best: radiology or radiotherapy? We, at HCG, also come across patients who wonder if radiodiagnosis is safe.
The answer depends on the medical need. Radiology focuses on diagnosis, treatment planning, and minor interventional procedures; radiodiagnosis predominantly focuses on diagnosis; and lastly, radiotherapy focuses on treating cancer.
Similarly, some wonder which is better, radiology or radiography—radiology involves medical imaging, while radiography is a subset focusing on X-ray imaging. Again, the right approach, in any case, depends on the patient’s specific medical needs.
Doctors determine the best course of action depending on the patient’s condition. Occasionally, all three disciplines are combined.
Understanding the difference between radiology and radiotherapy, along with radiodiagnosis, can provide key insights into how personalized healthcare can be and aid in informed decision-making.
Radiology focuses on diagnosis and minor interventions; radiodiagnosis approaches are used for the diagnosis of various diseases; and radiation therapy is used for cancer treatment.
As technology advances, the fields of radiology, radiodiagnosis, and radiotherapy continue to evolve, offering patients better diagnostic tools and more effective treatments

Dr. V. S. N. Rao
Director - Medical Services and Head of Radiation Oncology
MBBS, DMRT, MD (Radiation Oncology)
Dr. V. S. N. Rao is a senior radiation oncologist who is available for consultations at HCG Cancer Centre, a well-known comprehensive cancer hospital in Vijayawada. He has over 3 decades of experience in external radiotherapy and brachytherapy techniques. Dr. Rao has vast experience in treating cancers of the head & neck, breast, esophagus, gastrointestinal tract, lung, brain, and bones. He received specialized training in HDR & PDR brachytherapy at a reputed institute in Germany. Dr. Rao is committed to using the most advanced and personalized radiotherapy solutions for the best outcomes for cancer patients.
Appointment Link: Book an Appointment with Dr. V. S. N. Rao.