
07 Nov, 2025
Feel free to reach out to us.

07 Nov, 2025

This article is medically reviewed by Dr. Prabhu Nesargikar, Senior Consultant - GI and Peritoneal Cancer & Robotic Surgery, HCG Cancer Centre, K.R. Road, Bengaluru.
Gastrointestinal cancer is an umbrella term for cancers that affect the digestive tract and associated organs. The incidence of these cancers is on the rise in India, mainly due to changes in lifestyle and dietary habits, exposing themselves to more risk factors. Although a few GI cancers can be aggressive with poor treatment outcomes, most of them are preventable or can be detected at early stages through surveillance and screening.
By understanding the different gastrointestinal cancer symptoms, causes, and treatments, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their digestive health.
Read this article till the end to find out the best preventive measures against gastrointestinal cancers and how a leading cancer hospital in Bangalore, like HCG Cancer Centre, can help people win over cancer the right way, the first time.
Gastrointestinal cancer (GI cancer) develops when normal mucosal cells undergo changes leading to uncontrolled division that invades normal tissues and can spread throughout the body. GI cancer involves the digestive system: esophagus, stomach, colon and rectum, and surrounding organs like the liver, gallbladder, and pancreas. Depending on the type, GI cancers may develop or advance over the years or progress rapidly.
Initial stages are usually asymptomatic or have non-specific symptoms; that is why it is crucial to be checked up regularly and stay informed.
In 2022, India recorded 279,130 new cases of gastrointestinal cancer, according to the Globocan Reports, which accounted for 19.73% of all cancer cases. The increasing number of GI cancers contributes significantly to this emerging public health issue because they are often diagnosed late and have unique risk factors in some regions.
Depending on the organ affected by cancer, gastrointestinal cancers are categorized into different types. Each GI cancer type has different subtypes, symptoms, risk factors, and disease prognoses.
The following are the top 6 types of gastrointestinal cancers reported in India:
Esophageal cancer affects the tube that joins the mouth to the stomach. This is closely associated with smoking, drinking alcohol, obesity, and certain dietary habits, including chewing tobacco. Due to the absence of symptoms in early stages or the presence of vague symptoms, esophageal cancer is often diagnosed in later stages.
"Colorectal cancer" is a collective term given to colon cancer and rectal cancer. Risk factors include low-fiber diets, high red meat consumption, obesity, family history, and patients with inflammatory bowel disease, especially ulcerative colitis. Colorectal cancers have excellent 5-year survival rates in early stages.
Additional Reading: Why is colorectal cancer becoming more common among younger adults?
Stomach cancer, or gastric cancer, mostly results from smoking, chewing tobacco, consumption of diets with high salt, alcohol, obesity, and, more commonly, bacterial infections like Helicobacter pylori. Stomach cancer is found to be one of the common cancers in Bangalore.
Liver cancer often occurs due to chronic hepatitis B or C, excessive alcohol drinking, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. This is a fast-growing type of cancer that tends to be asymptomatic at the initial stages; however, some general signs such as fatigue, weight loss, and jaundice may occur.
Gallbladder cancer is more common in the regions of North and Northeast India. It is also more common in women. The risk factors are gallstones, long-standing cholecystitis, and obesity. Often diagnosed in later stages, gallbladder cancer has a poor prognosis.
Pancreatic cancer is one of the life-threatening gastrointestinal cancers since it is usually identified at an advanced stage because symptoms like abdominal pain, backache, jaundice, and loss of weight usually present at advanced stages of disease. The major risk factors are smoking, alcohol consumption, obesity, and chronic pancreatitis.
Appendix cancer, bile duct cancer, and small intestine cancer are some of the rare types of gastrointestinal cancer. Even though they are not common, these types can be aggressive, and hence, timely diagnosis is crucial for improved prognosis.
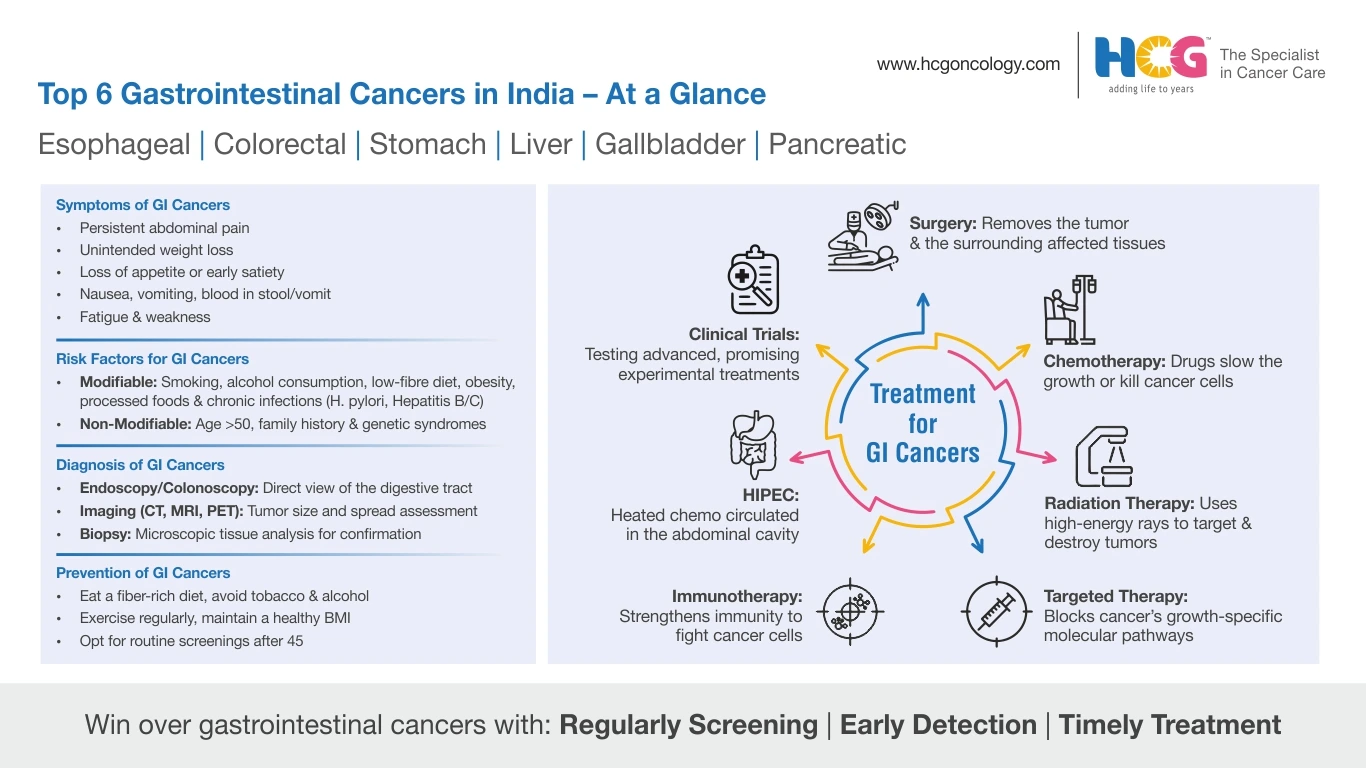
Gastrointestinal cancer symptoms may vary depending on the affected organ but often include:
Depending on the organ affected, symptoms of GI cancer can vary. The following are the symptoms of GI cancer, based on its type.
| Type of Gastrointestinal Cancer | Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Esophageal Cancer | Common symptoms include difficulty swallowing, food sticking in gullet, change in voice, vomiting blood |
| Colorectal Cancer | Common signs include diarrhea, constipation, blood in stool, black stools, abdominal pain |
| Stomach Cancer | Mainly observed signs include heartburn, recurrent vomiting, black stools, weight loss |
| Liver Cancer | Commonly observed symptoms include yellow eyes, a swollen belly, and getting bruises very easily. |
| Gallbladder Cancer | Signs to look for include agonizing pain under the ribs on the right side, vomiting, and yellow skin. |
| Pancreatic Cancer | Common symptoms include back pain, jaundice / yellow eyes, vomiting, |
While we don’t know the exact cause, we do know that certain factors increase the risk of GI cancer, and these factors are referred to as ‘risk factors.’
These risk factors are further classified into modifiable (lifestyle-based) risk factors and non-modifiable (non-lifestyle-based) risk factors.
The following are the risk factors or possible causes of gastrointestinal cancer:
Watch this video where Dr. Prabhu Nesargikar, our GI Surgical Oncologist from HCG Cancer Centre, Bangalore, explains how tobacco increases the risk of cancer development:
Different methods are used for gastrointestinal cancer diagnosis:
Early diagnosis is critical for positive gastrointestinal cancer treatment outcomes.
While planning gastrointestinal cancer treatment, doctors consider individual case parameters, such as the type of GI cancer, its stage and grade, the patient’s age, the overall health of the patient, and lastly, their preferences.
The following are the different GI cancer treatment options:
Surgery for gastrointestinal cancer aims at eliminating the tumor, along with a small portion of healthy surrounding tissues; it may also include resection of some parts of the alimentary canal.
Radiation therapy for gastrointestinal cancer involves the use of high-energy radiation beams to target and kill cancer cells, usually in combination with other therapies.
Chemotherapy for gastrointestinal cancer refers to the use of drugs to kill or slow cancer growth throughout the body. It can be given before or after surgery.
Targeted therapy for gastrointestinal cancer is an innovative cancer treatment approach wherein specific molecules and cellular pathways associated with cancer growth are targeted in order to control cancer growth.
Immunotherapy for gastrointestinal cancer involves re-engineering the immune system’s ability to identify and attack cancer cells.
Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy (HIPEC) involves delivering heated drugs directly to the abdominal cavity after surgically removing as much cancer tissue as possible.
Patients who have exhausted their GI cancer treatment options may opt for clinical trials that provide them access to new cancer-fighting drugs and treatments that are not yet available on the market.
| Type of Cancer | Treatments Commonly Recommended |
|---|---|
| Esophageal Cancer | Surgery (esophagectomy), chemotherapy, radiation therapy, combined chemoradiation, endoscopic mucosal resection (in very early stages), targeted therapy, and immunotherapy. |
| Colorectal Cancer | Surgery (colon or rectal resection), chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy. |
| Stomach Cancer | Gastrectomy (partial/total), chemotherapy, radiation therapy (in some cases), targeted therapy, and immunotherapy. |
| Liver Cancer | Resection, transplant, local ablation, TACE, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy. |
| Gallbladder Cancer | Radical Cholecystectomy, possible liver resection, chemotherapy, radiation therapy (in some cases) |
| Pancreatic Cancer | Whipple procedure, distal pancreatectomy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy |
For more information on personalized GI cancer treatment in Bangalore, please reach out to HCG.
Patients usually take the following steps during their recovery and monitoring:
Prevention strategies for GI cancer primarily include lifestyle modifications. Adopting a healthy lifestyle is critical to reducing the risk of different types of GI cancer.
The following are effective GI cancer prevention strategies:
Consume a lot of vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and fiber, and less processed foods and red meat.
Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate physical activity weekly.
Obesity is a major risk factor for several GI cancers—keeping a healthy BMI helps reduce risk.
Avoid smoking and limit alcohol intake to lower gastrointestinal cancer risk.
Precancerous changes can be detected early through routine screenings such as colonoscopy or endoscopy.
HCG Cancer Centre offers the best and most comprehensive cancer screening packages in Bangalore. Take one step towards proactive health with HCG’s health checkup packages.
As a leading cancer hospital in Bangalore, HCG Cancer Centre offers comprehensive treatment and management plans for different types of gastrointestinal cancer.
Its special focus on personalization and patient-centricity makes it one of the best hospitals for GI cancer treatment in Bangalore.
Helmed by a robust team comprising some of the best GI cancer specialists in Bangalore, the gastrointestinal oncology department here places a special emphasis on the quality of life of patients undergoing GI cancer treatment.
Gastrointestinal cancer is a serious health threat, but early detection and prevention can save lives. To enhance the results, it is important to recognize symptoms, understand causes, and seek treatment for gastrointestinal cancer.
With the right preventive measures and regular health checkups, it is possible to reduce the risk of various types of gastrointestinal cancer.
For more information on gastrointestinal cancer and its treatment, please visit HCG Cancer Centre, a well-known hospital for cancer treatment in Bangalore.

Dr. Prabhu Nesargikar
Senior Consultant - GI and Peritoneal Cancer & Robotic Surgery
MBBS, MRCS (RCSEng), MA (Medical Education), MD (Research), MFSTEd (RCSEd), FRCS (RCSEd), CCT (UK)
Dr. Prabhu Nesargikar is a highly experienced surgical oncologist, and his expertise lies in gastrointestinal robotic surgery, surgical gastroenterology, and advanced endoscopic surgery. He is available for consultations at HCG Cancer Centre, KR Road, Bangalore. He specialises in the management of all major GI malignancies, namely esophageal cancers, stomach cancer, small intestine cancer, and colorectal cancer, along with peritoneal malignancies. He takes a holistic approach to treatment and is committed to providing the best possible care for his patients
Appointment Link: Book an Appointment with Dr. Prabhu Nesargikar.