Table of Contents
What is Cancer?
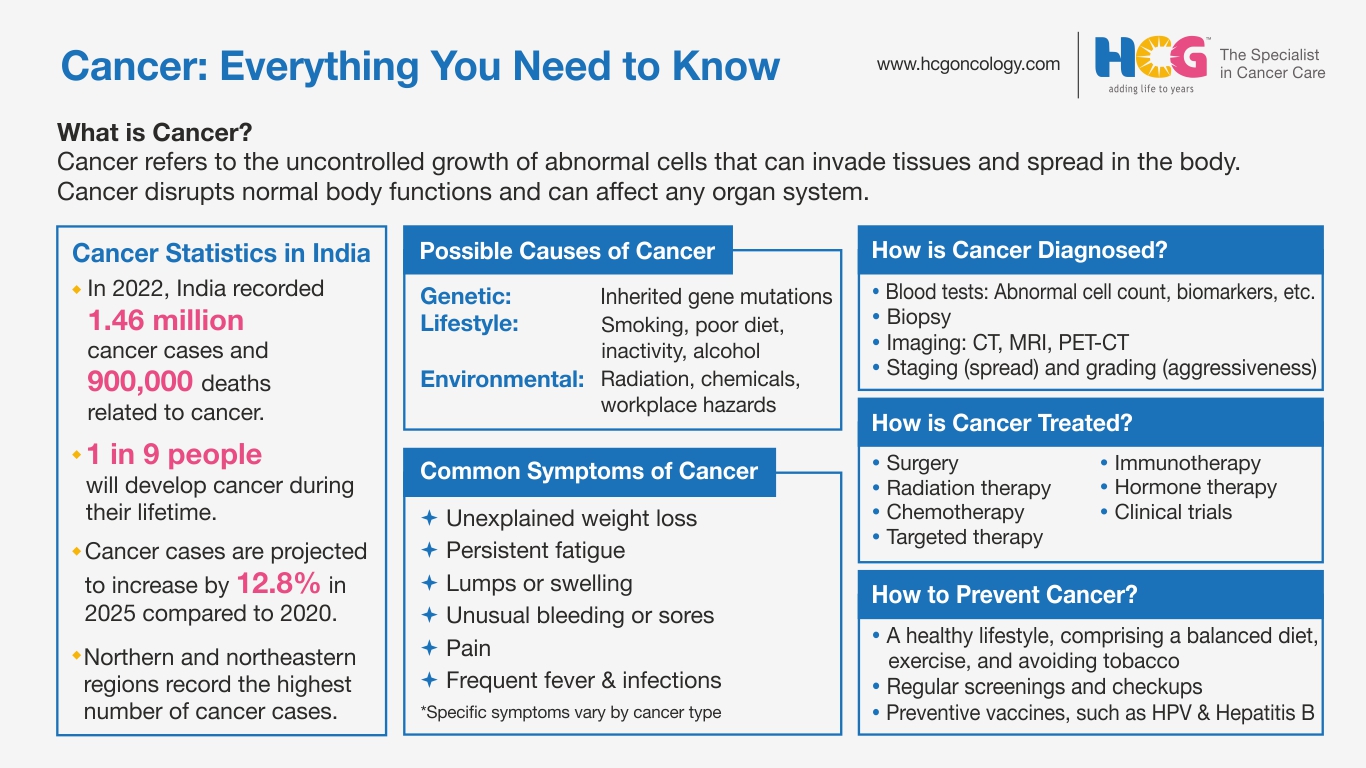
Cancer is a complex group of diseases characterized by the uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells in the body. These abnormal cells grow into primary tumors that, if left untreated, may invade surrounding tissues and metastasize to distant sites, thus disrupting normal body functions.
Being diagnosed with cancer can be an overwhelming experience, and it is one such disease that can drain patients and families alike physically, mentally, emotionally, and financially. This applies to all types of cancer—including the early-stage ones, advanced-stage ones, common ones, and rare ones.
Becoming aware of different types of cancer, as well as their signs and symptoms, risk factors, and possible ways they can be treated, can help in managing and potentially reducing the burden of this disease.
Understanding Cancer and Its Impact on the Body
At the cellular level, cancer starts when there are mutations in the DNA that interfere with normal cell growth as well as repair. These mutations may result in the development of tumors. Tumors can be classified as either:
-
Benign: Non-cancerous, contained or localized, and generally non-threatening.
-
Malignant: Cancerous, invasive, and capable of spreading to distant parts of the body.
Both benign and malignant tumors need prompt medical attention. Malignant tumors are best managed when they are diagnosed and treated in the early stages.
Types of Cancer
Most Common Types of Cancer
There are different types of cancer depending on their site of origin in the body. Some of the most frequent ones include:
-
Breast Cancer: It is a common disease among women globally, and regular screening through mammography can aid in its early detection and timely treatment.
-
Head and Neck Cancer: It is one of the most common cancers among Indian men, possibly due to excessive tobacco consumption. Regular screening promotes early detection and timely treatment.
-
Lung Cancer: It is closely linked to smoking and being around pollutants; high-risk individuals should consider regular screening for early detection.
-
Cervical Cancer: Cervical cancer is one of the slow-growing cancers, which can be treated with excellent outcomes if caught in the early stages.
-
Prostate Cancer: It is a common condition among elderly men. It can often be detected early through PSA tests.
-
Colorectal Cancer: The presence of precancerous polyps in the large intestine and rectum can lead to colorectal cancer. Regular health checkups play a pivotal role in their early detection and timely treatment.
-
Ovarian Cancer: Ovarian cancer causes vague symptoms in its early stages, and therefore, its timely diagnosis and treatment can be challenging.
Rare and Aggressive Forms of Cancer
-
Pancreatic Cancer: It does not show any symptoms in its early stages and grows rapidly. This makes its successful treatment challenging.
-
Leukemia: It affects the blood as well as the bone marrow by changing how new blood cells are made.
-
Brain Cancer: Certain types of brain cancer have a rapid growth rate and demand aggressive treatment regimens.
Becoming aware of different types of cancer, especially the common ones, can help one adopt appropriate preventive measures that help reduce their risk.
What Are the Causes of Cancer?
We do not know what exactly causes the cancer disease; however, we do know that certain factors can increase one’s chances of developing certain cancers. The risk factors or possible causes of cancer are multifactorial, including genetic factors, lifestyle, and environmental hazards.
Genetic Factors and Hereditary Cancer
Some forms of cancer are linked to gene mutations or inherited genetic disorders:
-
Gene Mutations: Having mutations in BRCA1 and BRCA2 raises the chances of getting breast, uterine, and ovarian cancers. Mutations in the ATM gene can increase the risk of prostate, pancreatic, and breast cancers. Mutations in the APC gene are associated with small intestine, large intestine, and pancreatic cancers. PTEN gene mutations are associated with kidney, thyroid, colorectal, and pancreatic cancers.
-
Familial Syndromes: Lynch syndrome is a known risk factor for colorectal cancer.
-
Family History of Cancer: When close members of the family are diagnosed with a particular type of cancer, it increases one’s chances of developing it. Those with a positive family history of cancer should consider genetic testing and counseling to learn about the degree of cancer risk they carry.
Lifestyle-Related Causes of Cancer
-
Smoking: A major contributor to lung, throat, and bladder cancers.
-
Unhealthy Food Habits: The risk of various cancers is higher in individuals who consume a lot of processed foods, sugary beverages, and red meat. Consumption of a diet that lacks essential macro- and micronutrients can also increase one’s cancer risk.
-
Physical Inactivity: A sedentary lifestyle contributes to a higher risk of developing cancer. Physical inactivity increases inflammation and causes hormonal imbalance in the body, which contributes to the increased risk of developing various types of cancer.
-
Obesity: A combination of unhealthy food consumption and physical inactivity leads to obesity, which causes chronic inflammation and hormonal imbalance, which increases the risk of different types of cancer.
-
Alcohol: Liver and esophageal cancers are associated with excessive drinking of alcohol. Alcohol consumption and smoking increase the risk of various cancers by multifolds.
-
Infections: Certain infections, if left unmanaged, can increase the risk of various types of cancer. A few such infections include HPV infection (cervical cancer), hepatitis B and C (liver cancer), Epstein-Barr virus (Hodgkin’s and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma), and H. pylori (stomach cancer).
-
Prolonged Exposure to UV Light: Prolonged exposure to UV rays can increase skin cancer risk.
Environmental and Occupational Risk Factors
- Exposure to Carcinogens: Asbestos and benzene are examples of carcinogens that can trigger cell mutations that can lead to cancer development.
- Radiation: Excessive exposure to ultraviolet rays as well as ionizing radiation for a long time can increase the chances of getting skin cancer.
Learning about the different possible causes of cancer helps in identifying strategies that help in reducing one’s cancer risk.
What Are the Symptoms of Cancer?
Certain cancers show symptoms in the early stages, while some don’t. The symptoms of cancer are often persistent, don’t respond to generic medicines, and do not get better with time.
Recognizing the signs of cancer is very important for a successful treatment.
Early Warning Signs of Cancer
- Unexplained weight loss
- Persistent fatigue
- Chronic pain or unusual lumps
- Changes in bowel or bladder habits
- Skin changes, such as moles that grow or bleed
Symptoms by Type of Cancer
-
Head and Neck Cancer Symptoms: Persistent sore throat, difficulty swallowing, hoarseness or changes in voice, unexplained weight loss, ear pain, and presence of a lump in the throat/neck region.
-
Lung Cancer Symptoms: Persistent cough, chest pain or discomfort, shortness of breath, frequent lung infections, hoarse voice, intentional weight loss, and tiredness.
-
Breast Cancer Symptoms: Lumps, nipple discharge, changes in the texture of breast skin, or changes in breast shape.
-
Gastrointestinal Cancer Symptoms: Blood in stool, nausea and vomiting, sense of fullness after consuming small quantities of food, jaundice, changes in bowel movements, abdominal pain, and unexpected weight loss.
-
Gynecological Cancer Symptoms: Abnormal vaginal bleeding or discharge, pelvic pain or pressure, bloating, frequent urge to urinate, and pain during or after intercourse.
-
Urological Cancer Symptoms: Blood in the urine, frequent urination, painful urination, lower back pain, difficulty starting urination, fatigue, and unintended weight loss.
-
Orthopedic Cancer Symptoms: Swelling or tenderness in bones, persistent bone pain, bone fractures, severe tiredness, and unintended weight loss.
-
Blood Cancer Symptoms: Fatigue and weakness, frequent infections, unexplained weight loss, easy bruising or bleeding, swollen lymph nodes, and bone pain.
Awareness of cancer symptoms facilitates early consultation and diagnosis.
How is Cancer Diagnosed?
Timely cancer diagnosis improves treatment success and survival rates.
Tests and Procedures Used to Detect Cancer
-
Imaging Tests: The detection of abnormalities in the body is highly dependent on imaging techniques such as X-rays, CT scans, MRIs, and PET scans. These tests are important in determining the location, size, and extent of tumors. These tests are extremely helpful in disease staging, treatment planning, and treatment response monitoring.
-
Biopsies: To confirm cancer, a small tissue sample is collected from the suspected area and examined under a microscope. There are different ways of taking biopsies, such as needle aspiration, surgical excision, or endoscopic procedures. A biopsy aids in the confirmative diagnosis of cancer.
-
Blood Tests: Certain cancers release substances called tumor markers into the bloodstream. For example, PSA (Prostate-Specific Antigen) in prostate cancer or CA-125 in ovarian cancer.
-
Endoscopy: In some cases, doctors use an endoscope—a thin, flexible tube with a camera—to view the inside of the body and collect tissue samples. This method is commonly used for gastrointestinal cancers, such as colorectal or esophageal cancer.
Staging and Grading in Cancer Diagnosis
-
Staging: Staging evaluates how far cancer has spread within the body. It is categorized into 4 stages: Stage 0 refers to the stage where the disease is localized, while Stage IV refers to the stage where the disease has spread to various nearby and distant organs.
-
Grading: The grading is based on the degree of abnormality exhibited by cancer cells under a microscope. In most cases, low-grade tumors are slow to develop and metastasize; on the other hand, high-grade tumors tend to be very aggressive with a rapid growth rate.
Advances in cancer diagnosis have made it possible to detect cancer at earlier stages, which has led to better treatment outcomes.
What Are the Cancer Treatment Options?
The treatment of cancer depends on the type, extent, and general well-being of the patient.
1. Surgery and Its Role in Cancer Treatment
The initial treatment for localized tumors is usually surgery. It can be curative when cancer is detected early.
There are different surgical approaches available for cancer patients, depending on the individual care needs.
Additional Reading: Here is a detailed article on how surgery helps in the effective management of different types of cancer: 14 Types of Cancer Surgeries: Pros, Side Effects & Surgical Options | HCG
2. Radiation Therapy: How It Works
This treatment approach uses high-energy radiation beams to precisely target cancer cells while minimizing damage to surrounding tissues. It is effective in treating localized cancers or shrinking tumors before surgery.
Additional Reading: Radiation therapy is a non-invasive treatment approach for cancer. Read this article for a detailed understanding of how radiation therapy is used in cancer management: What is Radiation Therapy - Procedure, Tests & Risks
3. Chemotherapy and Targeted Therapy Explained
-
Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy involves the administration of powerful anti-cancer drugs to destroy cancer cells throughout the body. Side effects can include nausea, fatigue, and hair loss.
-
Targeted Therapy: This treatment approach involves targeting specific proteins and pathways associated with cancer growth and devising a precise treatment approach that has minimal side effects.
Additional Reading: Chemotherapy is a systemic therapy against cancer, and it is one of the main pillars of cancer treatment. Click on this article to know chemotherapy destroys cancer cells in the body: Exploring Types of Chemotherapy Treatments
Wondering how chemotherapy is different from radiation therapy in managing cancers? Read this article as one of our specialists explains the key differences between chemotherapy and radiation therapy: Chemotherapy vs Radiation Therapy - What's the Difference?
4. Immunotherapy: Boosting Your Body’s Defenses
This innovative treatment approach enhances the immune system’s ability to identify and attack cancer cells. Its effectiveness has been demonstrated in melanoma and some forms of lung cancer.
Learning about the different cancer treatment options empowers patients to make informed decisions about their care.
Additional Reading: Immunotherapy is one of the latest forms of cancer treatment that has shown promising results in recent times. Here is a detailed article on how this treatment targets cancer cells: Immunotherapy: The Fourth Pillar of Cancer Treatment | HCG
How to Prevent Cancer?
While no cancer is 100% preventable, the risk of developing certain cancers can be reduced with appropriate preventive measures.
1. Lifestyle Changes to Reduce Cancer Risk
-
Avoid Tobacco: Quitting smoking significantly reduces the risk of lung and throat cancers.
-
Adopt a Healthy Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains promotes overall well-being and reduces cancer risk.
-
Embrace Physical Activity: Regular exercise helps maintain a healthy weight, lowering cancer risk.
Additional Reading: Want to learn more about reducing your cancer risk? Read this article where one of our specialists shares the key measures one can adopt to reduce cancer risk: 7 Best Ways to Reduce Your Cancer Risk - HCG
2. Importance of Regular Screenings and Checkups
Early detection of precancerous conditions is possible through tests like mammograms and colonoscopies. Self-examinations and routine checkups are crucial in identifying early signs of cancer.
3. Vaccines and Their Role in Cancer Prevention
-
HPV Vaccine: Prevents cervical and throat cancers caused by the human papillomavirus.
-
Hepatitis B Vaccine: Reduces the risk of liver cancer linked to hepatitis B.
Focusing on the prevention of cancer is one way to reduce its risk effectively.
Conclusion
Although cancer is a formidable challenge, it can be dealt with effectively through early detection, proper treatment, and prevention. People can shield themselves by knowing what cancer is, its causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
With ongoing research and innovation, the fight against cancer continues, offering hope and improving outcomes for millions affected by this complex disease. A combination of healthy living, frequent check-ups, and immunizations can greatly lower the chances of getting cancer.
At HCG, a leading cancer hospital in India, we provide comprehensive cancer care, including screening, diagnosis, treatment, follow-up, rehabilitation, and palliative care. This positions HCG as the one-stop solution for all cancer-related inquiries.
Frequently Asked Questions
References