
02 Dec, 2025
Feel free to reach out to us.

02 Dec, 2025

This article is medically reviewed by Dr. B. J. Srinivas, Senior Consultant - Medical Oncology, HCG Cancer Centre, Bengaluru.
Cancer occurs when there are specific, undesirable mutations in the DNA structure of healthy cells, which will cause abnormal or uncontrollable cell division.
Proto-oncogenes, which are part of the DNA present in healthy cells, regulate key functions of the cell cycle, including cell growth and differentiation. Mutations in these genes give rise to oncogenes that lead to cancer development.
This article discusses genetic mutations that contribute to cancer development and the different risk factors that increase one’s cancer risk and answers some of the burning questions associated with various causes of cancer.
It is a common assumption that only those with a family history of cancer have a higher risk of being diagnosed with this condition. However, it is only partly true. Someone who has not inherited cancer-causing mutations can also be diagnosed with cancer because they developed a mutation after they were born.
Gene mutations are of two types: inherited and acquired.
1. Inherited gene mutations occur in the germline cells (egg and sperm) of the parents and are passed on to the offspring or child. Examples include BRCA1 and 2 mutations and Lynch syndrome.
2. Acquired genetic mutations, on the other hand, occur in somatic cells (cells other than sperm and egg) in specific parts of the body and are not passed on to offspring. Several lifestyle and environmental factors may contribute to these mutations, eventually leading to abnormal cell division. Examples include p53 mutations from smoking and UV-induced mutations.
The following table sheds light on the dynamics of inherited gene mutation vs. acquired gene mutation:
| Feature | Inherited Mutation | Acquired Mutation |
|---|---|---|
| Place of Origin | Germline cell of the parent (egg or sperm) | Somatic cells present in different parts of the body |
| Presence in Body | Present in every cell of the child/offspring | Present only in affected cells |
| Time of Occurrence | Present at birth | Can occur anytime in an individual’s lifetime. |
| Degree of Cancer Risk | Causes about 5-10% of cancers | Causes about 90-95% of cancers |
| Heritability | Passed on to the next generations | Not passed on to the next generations |
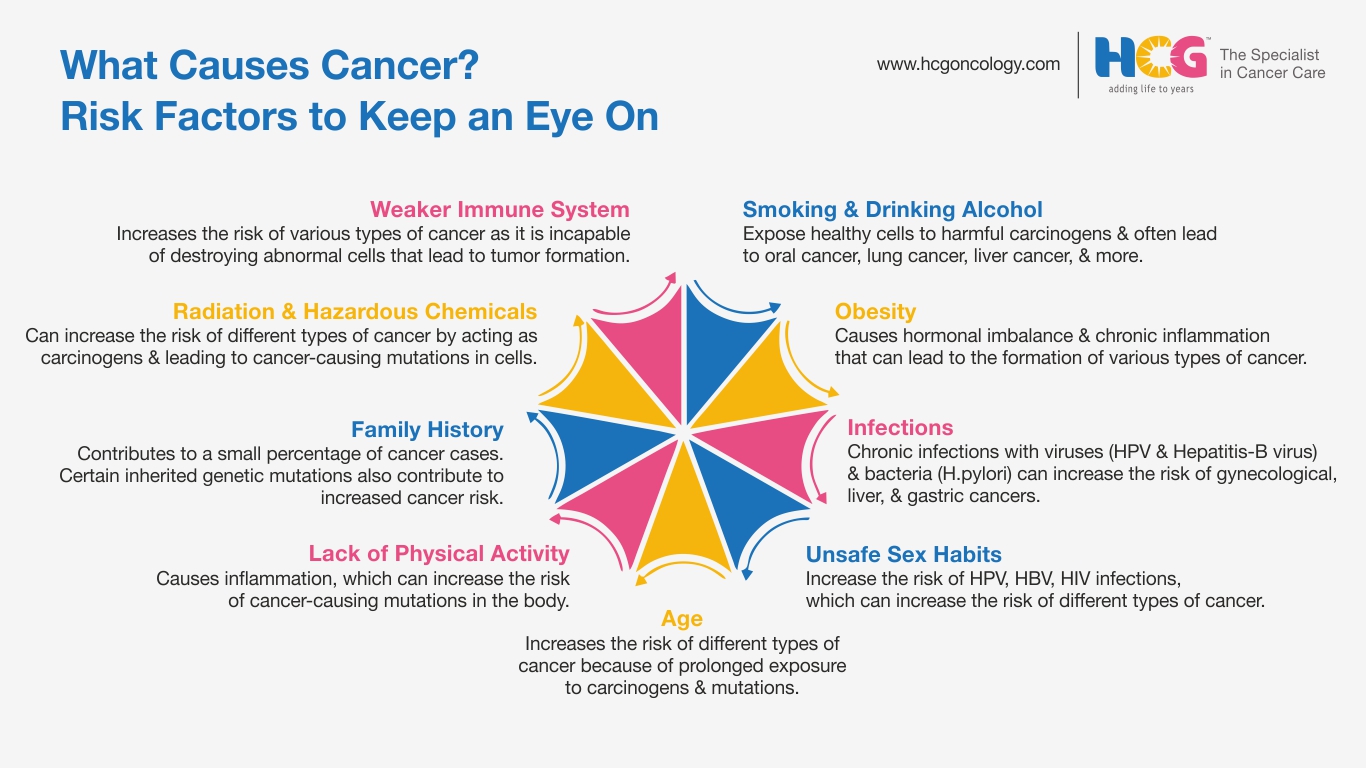
While we know that genetic mutations lead to cancer development, we are yet to understand what exactly causes these genetic mutations. Over the years, we have studied that certain factors can increase the risk of cancer-causing mutations, and they are called risk factors or potential causes of cancer.
Many believe that smoking cigarettes causes cancer. The answer is true.
Tobacco consumption is identified as one of the biggest risk factors for cancer development. Tobacco has harmful carcinogens, which can induce cancer-causing mutations in the DNA of cells in the body.
Tobacco is reported to increase the risk of at least 15 types of the most common cancers, including lung cancer, oral cancer, throat cancer, bladder cancer, and kidney cancer.
Both smoking and chewing tobacco carry significant cancer risk; additionally, secondhand smoking causes cancer among non-smokers.
Alcohol consumption is also identified as an important cancer risk factor. When consumed, it produces acetaldehyde, which is a toxic byproduct capable of damaging the DNA structure.
Further, when combined with tobacco consumption, the cancer risk is amplified, as alcohol makes cells more susceptible to absorbing the carcinogens.
Excessive alcohol consumption is linked to cancers of the liver, breast, esophagus, colon, and rectum.
Obesity is also identified as one of the biggest risk factors for cancer, as it causes chronic inflammation and hormonal imbalance in the body, which may eventually lead to tumor growth.
A high-fat, low-fiber, and high-calorie diet can lead to obesity. This risk factor is associated with the development of breast cancer, colorectal cancer, endometrial cancer, and pancreatic cancer.
A sedentary lifestyle can lead to obesity and hormonal imbalance, which are identified as risk factors for cancer development.
In simple words, a lifestyle that causes cancer may include unhealthy eating habits, lack of physical activity, and obesity that occurs as a result.
A lack of physical activity may increase the risk of breast cancer, lung cancer, colon cancer, endometrial cancer, and more.
Certain inherited genetic conditions and a family history of cancer are also identified as important risk factors for tumor growth.
Commonly observed inherited genetic conditions that can increase cancer risk include familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP), Lynch syndrome, Li-Fraumeni syndrome, von Hippel-Lindau (VHL), BRCA1 and 2 mutations, multiple endocrine neoplasia, and more.
Having more than 2 members of the family diagnosed with the same type of cancer, or having multiple family members diagnosed with different types of cancer, can increase one’s cancer risk as well.
Additional Reading: Is Cancer Genetic? | HCG
Unsafe sex habits, such as unnatural sex practices, not using safety measures, and having multiple sexual partners, may cause chronic viral infections, which increase the risk of certain cancers.
HPV infection is a sexually transmitted disease, which, if left unmanaged can cause cervical cancer, vaginal cancer, vulvar cancer, anal cancer, oropharyngeal cancer, and more.
HIV infection, on the other hand, weakens the immune system, causing the abnormal cells to proliferate more readily and form a tumor.
Additional Reading: Can Chronic HPV Infection Cause Head & Neck Cancer | HCG
Exposure to ionizing radiation from previous cancer treatments or ultraviolet radiation from sunlight can cause damage to the DNA structure and lead to the growth of cancer cells.
Prolonged exposure to harmful chemicals, either at the workplace or at home, can also contribute to increased cancer risk.
Additionally, certain skincare, haircare, and cosmetic products can increase the risk of cancer due to the harmful chemicals present in them. Their regular use can increase the risk of various types of cancer.
In the next section, this risk factor is discussed extensively.
Viral infections, such as HPV, hepatitis B and C, and HIV, and bacterial infections, such as Helicobacter pylori infection, are also identified as risk factors for cancer.
This risk factor is discussed in detail in the upcoming sections.
Increasing age is a non-modifiable risk factor for cancer.
Prolonged exposure to risk factors, higher prevalence of chronic health conditions like obesity and diabetes, and accumulation of genetic mutations over the years are some factors that contribute to increased cancer risk among aged populations.
A compromised immune system may not be efficient in destroying abnormal cells that may lead to cancer development.
Certain infections, organ transplants, and certain autoimmune conditions can weaken the immune system and increase the risk of various types of cancer.
Yes, in some cases, an individual’s working and housing conditions can contribute to their cancer risk. Exposure to certain hazardous chemicals and radiation at work and at home contributes to a small percentage of cancer cases.
Radiation exposure from previous cancer treatments, prolonged exposure to radon gas (a radioactive byproduct of uranium), which is especially found in buildings with cracks, holes, gaps, and other openings, and frequent radiation exposure at tanning beds can increase the risk of cancers, such as lung cancer, blood cancer, breast cancer, skin cancer, and certain types of sarcomas.
Living or working in polluted areas can increase one’s lung cancer risk. Vehicle exhaust, industrial emissions, dust storms, wildfires, mining and quarrying, and certain household activities increase the levels of harmful pollutants in the environment.
Hazardous pollutants that can increase the risk of lung cancer and other types of cancer include PM 2.5 (particulate matter), volatile organic compounds (VOCs), aromatic hydrocarbons (benzene, toluene, naphthalene, etc.), and nitrogen oxides.
Reducing exposure to these pollutants with appropriate measures like wearing N95 masks and the use of air filters can help reduce the risk of lung cancer and other cancers.
Individuals working in the industries of printing, textiles, plastics, rubber, leather, and refineries, among others, have a relatively higher risk of developing cancer when compared to those who don’t.
To reduce exposure to harmful carcinogens, one should consider using appropriate personal protective equipment, ensuring proper ventilation, and following personnel safety protocols.
The use of skincare and haircare products containing harmful carcinogens may also be identified as one of the reasons for cancer development.
Certain products contain compounds like formaldehyde, parabens, benzene compounds, phthalates, heavy metals, certain elements like mercury, cadmium, and arsenic, and fragrances, which have carcinogenic properties and can increase cancer risk with prolonged exposure.
Therefore, one must choose skincare, haircare, and cosmetic products that are free from these carcinogens.
Yes, certain viral and bacterial infections can contribute to 15-20% of cancer cases. Common viral infections that increase the risk of cancer development include:
Having these viral and bacterial infections does not guarantee a cancer diagnosis. However, they do increase the risk, particularly if left unmanaged for an extended period and become chronic.
Being attentive to infection symptoms and seeking necessary medical attention can help reduce the risk of various types of cancer.
HCG is one of the leading chains of comprehensive cancer hospitals in India. It is widely known for its cutting-edge cancer diagnosis and treatment facilities. HCG is equipped with dedicated departments to facilitate organ-specific care.
Our multidisciplinary care team thoroughly evaluates each cancer case to understand the underlying causes and identify individual case factors before recommending an individualized treatment plan. Our personalized and patient-focused treatment approach contributes to better health outcomes and improves patients' quality of life.
Cancer forms when DNA mutations in healthy cells lead to uncontrolled cell division. These mutations could be somatic, acquired in an individual’s lifetime through association with various risk factors, including lifestyle and environmental factors, or genetic, inherited from parents.
To adopt effective cancer prevention strategies, it is essential to be aware of the different risk factors associated with cancer development. Since obesity, poor food habits, a sedentary lifestyle, tobacco and alcohol consumption, certain infections, and exposure to radiation and hazardous chemicals have been identified as key risk factors for cancer, it is essential to devise preventive measures that counter these risk factors.

Dr. Srinivas B. J.
Senior Consultant - Medical Oncology
MBBS, MD (General Medicine), DNB (Medical Oncology)
Dr. Srinivas is a senior medical oncologist who specializes in treating and managing solid and hematological tumors. He is available for consultations at HCG Cancer Centre, a top-ranking cancer hospital in Bengaluru. He has a special interest in the management of solid cancers in the breast, lung, prostate, colorectal, and sarcomas. Dr. Srinivasa practices precision care in cancer diagnosis and management through genomic-based cancer treatment.