
22 Dec, 2025
Feel free to reach out to us.

22 Dec, 2025

This article is medically reviewed by Dr. Moumita Bag, Associate Consultant - Gynecologic Oncology, HCG Cancer Centre, Nagpur.
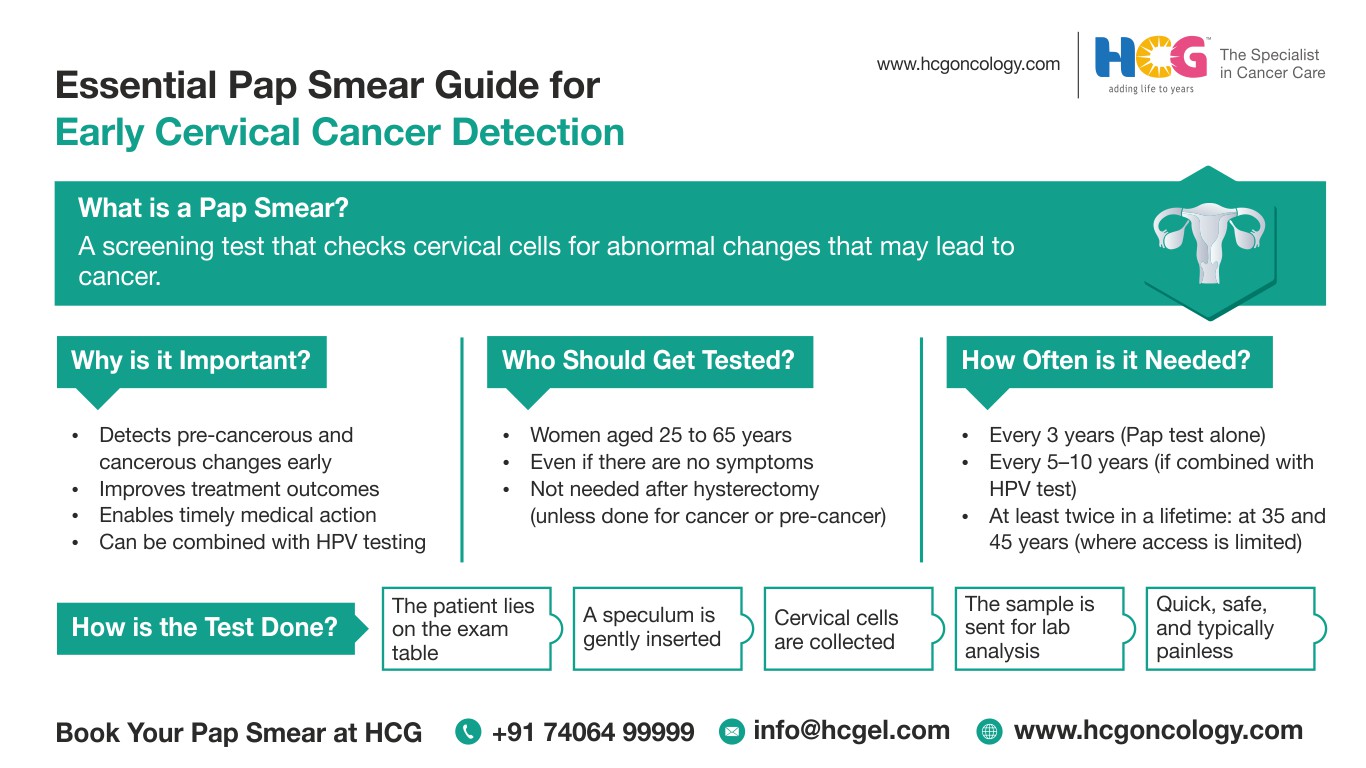
A Pap test is a widely performed screening test to detect cervical cancer or precancerous conditions by examining the collected cervical cells under a microscope for any abnormalities.
It assists in the detection of cervical precancerous conditions and thus improves the chances of early detection of cervical cancer, which, in turn, increases the chances of cure and survival.
The Pap smear test is of two types: conventional and liquid-based cytology (LBC Pap smear).
The conventional Pap smear test involves collecting samples from the cervical lining and directly placing the sample on the slide for microscopic examination.
Liquid-based cytology, on the other hand, involves collecting the sample into a liquid preservative. This method allows for better cell preservation.
LBC Pap smear samples can be used to detect high-risk HPV (Human Papillomavirus) DNA during primary hrHPV testing, co-testing (using the LBC Pap smear for both cytology and HPV DNA testing), and reflex HPV DNA testing, which is a follow-up test performed on the same sample after cytology analysis of the LBC Pap smear test sample suggestive of low-grade abnormalities to detect the presence of high-risk HPV DNA.
The Pap smear test is an important cervical cancer screening tool. It detects precancerous cells in the cervix at an early stage.
The test also enables doctors to detect infections, inflammation, or cellular changes caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). These factors enhance the cervical cancer risk.
A Pap smear procedure is generally performed in conjunction with a pelvic examination.
It is important to have a clinical examination done by an experienced doctor for interpretation of the Pap smear report and a proper, evidence-based cervical cancer treatment strategy as per guidelines.
It is a screening test that does not depend on the patient’s complaints (symptoms).
Additional Reading: Cervical Cancer Screening Test at HCG Oncology
Women should avoid douching, vaginal sex, vaginal creams, tampons, medications, and pessaries 2 to 3 days before the Pap smear test.
Conventional Pap smear tests are not performed during menstrual periods, but LBC Pap smear screening tests can be performed even during periods. The chance of having an unsatisfactory smear for analysis is much less for the LBC Pap smear test.
Nonetheless, it is better to avoid the tests during menstruation altogether.
If there was a pelvic examination done in the past 24 hours or a cervical procedure in the last 6 weeks, the Pap smear should be avoided.
For a detailed understanding of how the Pap smear test is done, one may talk to their gynecologist/gynec-oncologist.
The following are the Pap smear steps:
The patient may experience mild spotting after the test. Most patients feel fine and can start their daily activities just after the test.
Slight bleeding is normal after the test; however, patients do not need doctor supervision post-procedure because there is no chance of heavy bleeding, fever, chills, discharge with a foul smell, or severe abdominal pain post-procedure unless the patient had any pre-existing vaginal or cervical infection.
It's generally recommended to delay the Pap smear until after a vaginal infection is treated. This is because the infection can potentially interfere with the accuracy of the Pap smear results.
Discuss the Pap smear test results with your healthcare provider. It is an important step to know the pattern of management.
Just having a Pap smear test is not enough; it is recommended to have a discussion on the reports with the doctor (whether normal or abnormal) for appropriate guidance on the necessary interventions.
Although the Pap smear test for cervical cancer screening is a safe, quick, and effective screening tool for cervical cancer, it may have some minor discomfort.
Patients may experience discomfort or mild spotting after the test.
Although pain and cramping after the test are not very common, they may occur in some patients.
False-negative results may occur in rare cases. It may be due to the collection of a very small number of sample cells, the presence of infection or blood, or the removal of cells by douching or vaginal medications.
As per the latest guidelines by FOGSI-ICOG, the following are cervical cancer screening recommendations through Pap smears for different age groups:
| What is Recommended | Recommendation Grade/Level of Evidence | |
|---|---|---|
| At what age should the screening start? |
In a good resource setting: 25 years Universal recommendation: 30 years |
Level 1, Strong Recommendation |
| At what age should the screening end? |
65 years with 3 consecutive negative
cytology results OR
2 consecutive negative HPV tests within
10 years Note: The most recent test should have been performed within 5 years. |
Level 1, Strong Recommendation |
| Tests for the screening interval |
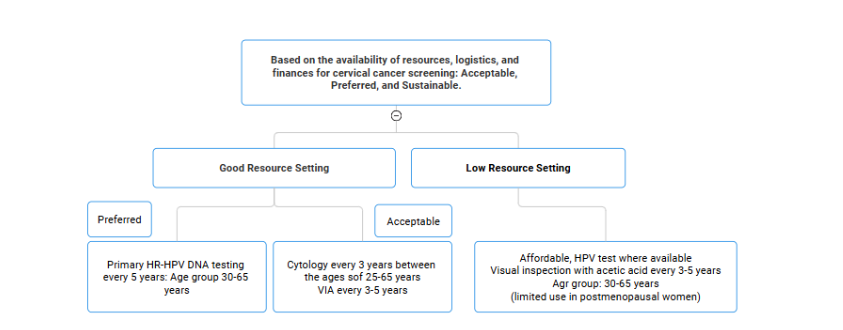
Primary hrHPV testing 1. Good resource settings: every 5–10 years in 2. Limited resource settings: At least twice in a lifetime, i.e., at 35 years and 45 years Cytology: every 3 years VIA: every 3–5 years |
Level 1, Strong Recommendation |
| Undergoing screening after hysterectomy with cervix removal | Screening is not recommended in normal circumstances. However, screening continues if the hysterectomy was done for cancer or a precancerous condition. | Level 1, Strong Recommendation |
| Screening for women with a compromised immune system | Screening to start at 25 years. Screening should be done more frequently; the duration between two screenings should not extend beyond 3 years. It is preferable to screen with HPV tests. | Level 1, Strong Recommendation |
Screening recommendations based on resource settings:
As mentioned previously, a conventional Pap smear has the limitation that it is for cytology abnormality interpretation (precancerous and cancerous abnormalities).
But the LBC Pap smear is a high-performance test with feasibility for the detection of cytology abnormalities and HPV DNA testing to detect high-risk HPV as per the choice of type of Pap smear testing.
This comprehensive guide by HCG covers key aspects associated with Pap smear tests, along with answering questions like, “What is a Pap smear test, and how is it done?”
The Pap smear test is a safe, simple, quick, and effective screening test for detecting abnormal or precancerous conditions in the cervix. The test involves collecting the cervical cells for microscopic examination. The frequency of Pap smear tests is as per the guidelines of FOGSI-ICOG.
The FOGSI (The Federation of Obstetric and Gynecological Societies of India)-ICOG (Indian College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists)’s GCPR (Good Clinical Practice Recommendations) guidelines aid in the prevention and management of cervical cancer and precancerous abnormalities. Various other international organizations, including ACOG and USPSTF, have recommended it. Patients should follow their doctor's instructions before, during, and after the Pap smear screening test. The test is usually well tolerated, with only mild discomfort.

Dr. Moumita Bag
DNB-OBGY, AGOI Fellowship in Gynecologic Oncology; Fellowship in Laparoscopic & Robotic Surgery
Dr. Moumita Bag is a gynecologic oncology consultant with over 7 years of experience. She can be consulted at HCG Cancer Centre, a well-known comprehensive cancer hospital in Nagpur. She has completed specialized training in laparoscopic and robotic surgery. Her expertise lies in gynecological malignancies, robotic surgery, laparoscopic surgery, pre-invasive gynecological diseases, gynecological cancer screening, cytoreductive surgeries, exenteration, radical hysterectomy, and fertility-sparing surgeries.
Appointment Link: Book an Appointment with Dr. Moumita Bag